In modern ITSM and ITAM systems, one of the key elements that organizes daily work is the logical division of objects into locations and departments. This applies to IT asset records and inventory, as well as ticket handling in the ticketing system, the knowledge base, notes, approvals, and confirmations. A clear structure helps maintain order, improves visibility control, and makes it easier to navigate data regardless of the organization’s size.
Locations - a service model divided into companies, departments, sections, and rooms
The location mechanism in Codenica ITSM + ITAM is one of the core foundations for organizing data across asset records, inventory, the ticketing system, and other application modules. The concept has been designed to be flexible, meaning that the same fields can be used both by companies servicing multiple external organizations and by organizations using the system internally only. This flexibility allows the same structure to be reused across different business models without redefining data relationships.
- IT service providers working with multiple clients
- The Location field is best used as the name of the serviced company.
- The Department field represents the client’s organizational unit, operational division, or internal structure.
- Organizations using the system internally
- The Location field can represent organizational departments (e.g., IT, HR, Accounting).
- The Department field can define an internal organizational unit or office context.
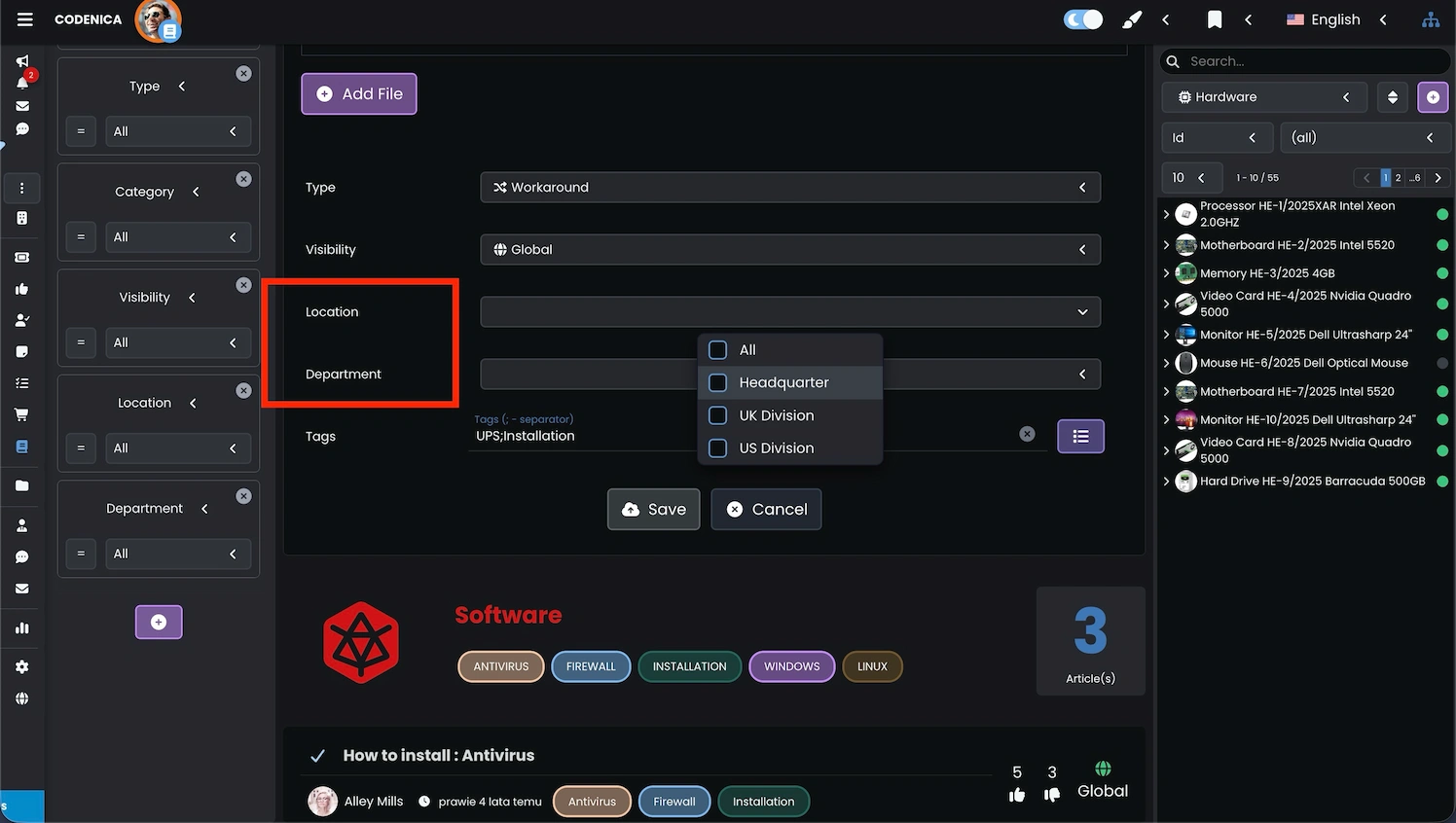
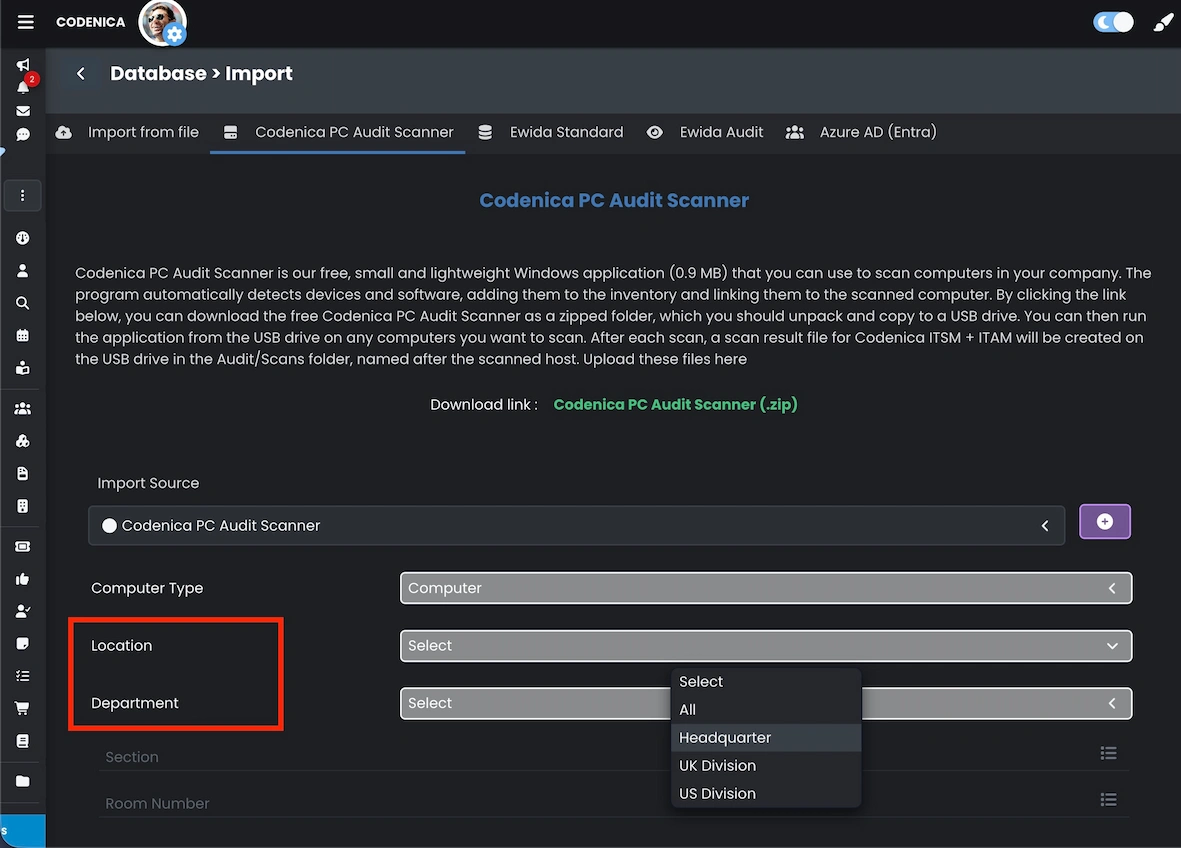
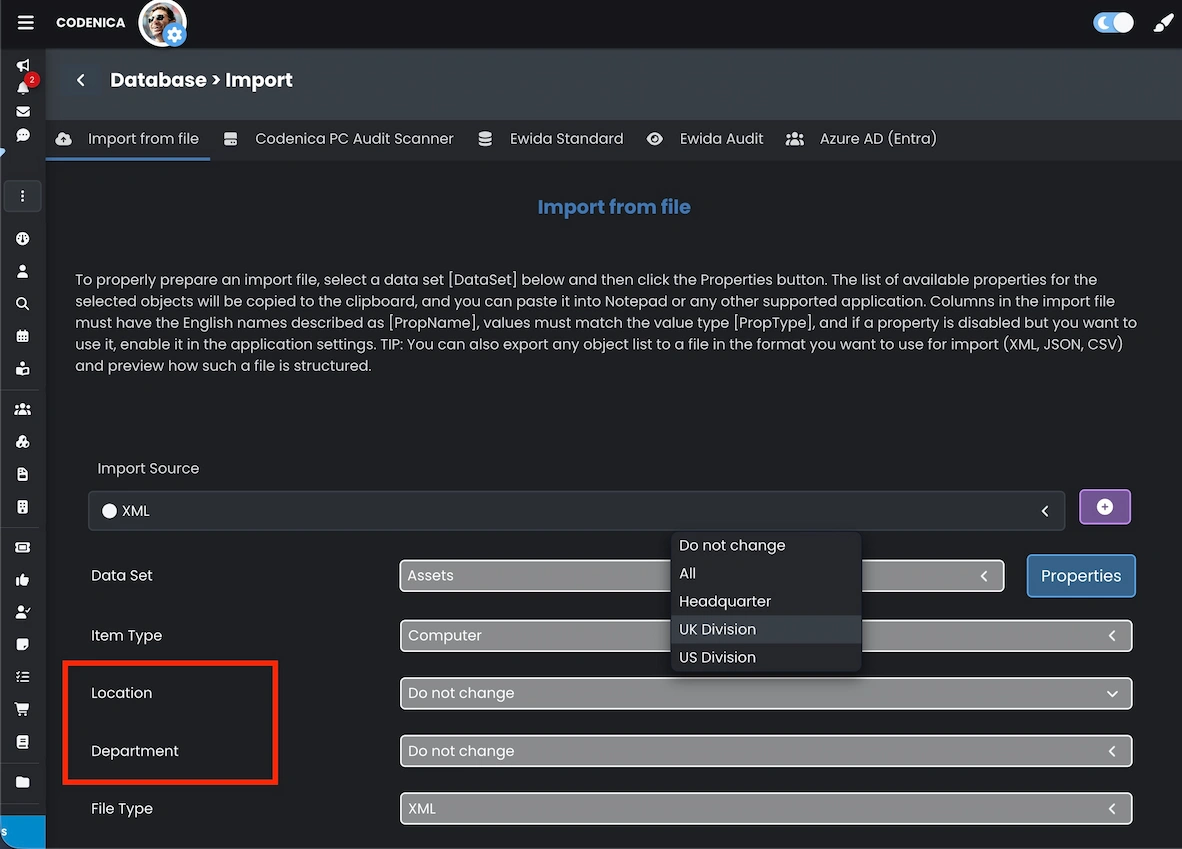
Additionally, the location mechanism allows very precise physical placement of objects using two complementary fields:
- Section - for example, a floor, building wing, zone, or separated area.
- Room number - the exact physical location of the object.
Thanks to this approach, Location and Department provide a logical, organizational structure, while Section and Room Number add physical precision.
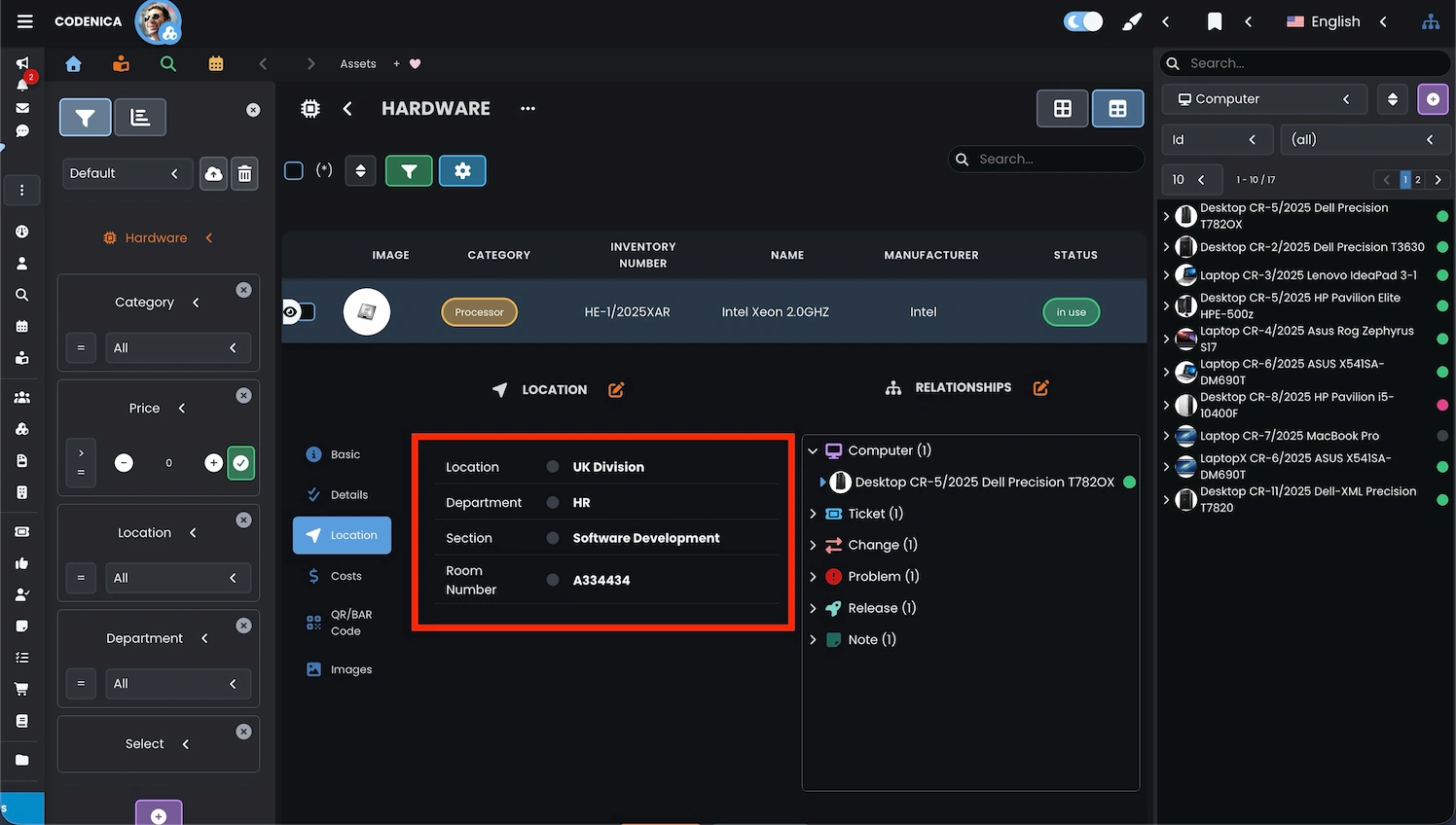
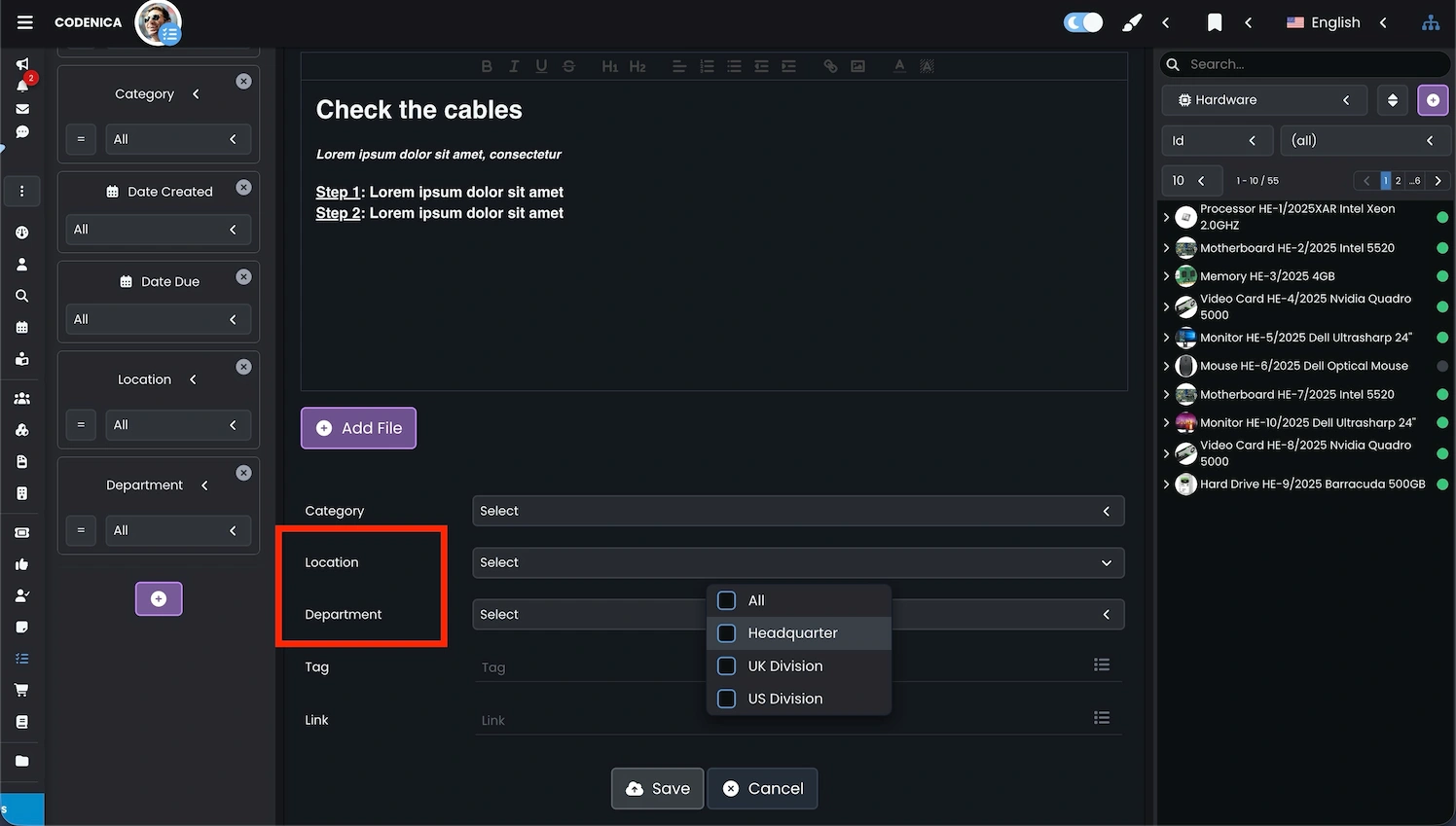
Assigning locations in asset records and inventory
In IT asset records and inventory, logically assigning objects to an organizational structure is crucial for maintaining order and data consistency. This applies to all infrastructure components such as computers, network devices, peripherals, licenses, and software. Each asset gains a clear organizational and operational context, which significantly improves daily IT operations-especially in environments where the number of assets grows dynamically.
This approach makes asset records and inventory clear and easier to manage. Well-defined assignment helps identify assets faster, analyze their placement, and plan administrative and technical activities. These data are used in reports, audits, compliance checks, and IT asset control processes, turning inventory into a practical source of operational knowledge rather than just a static list.
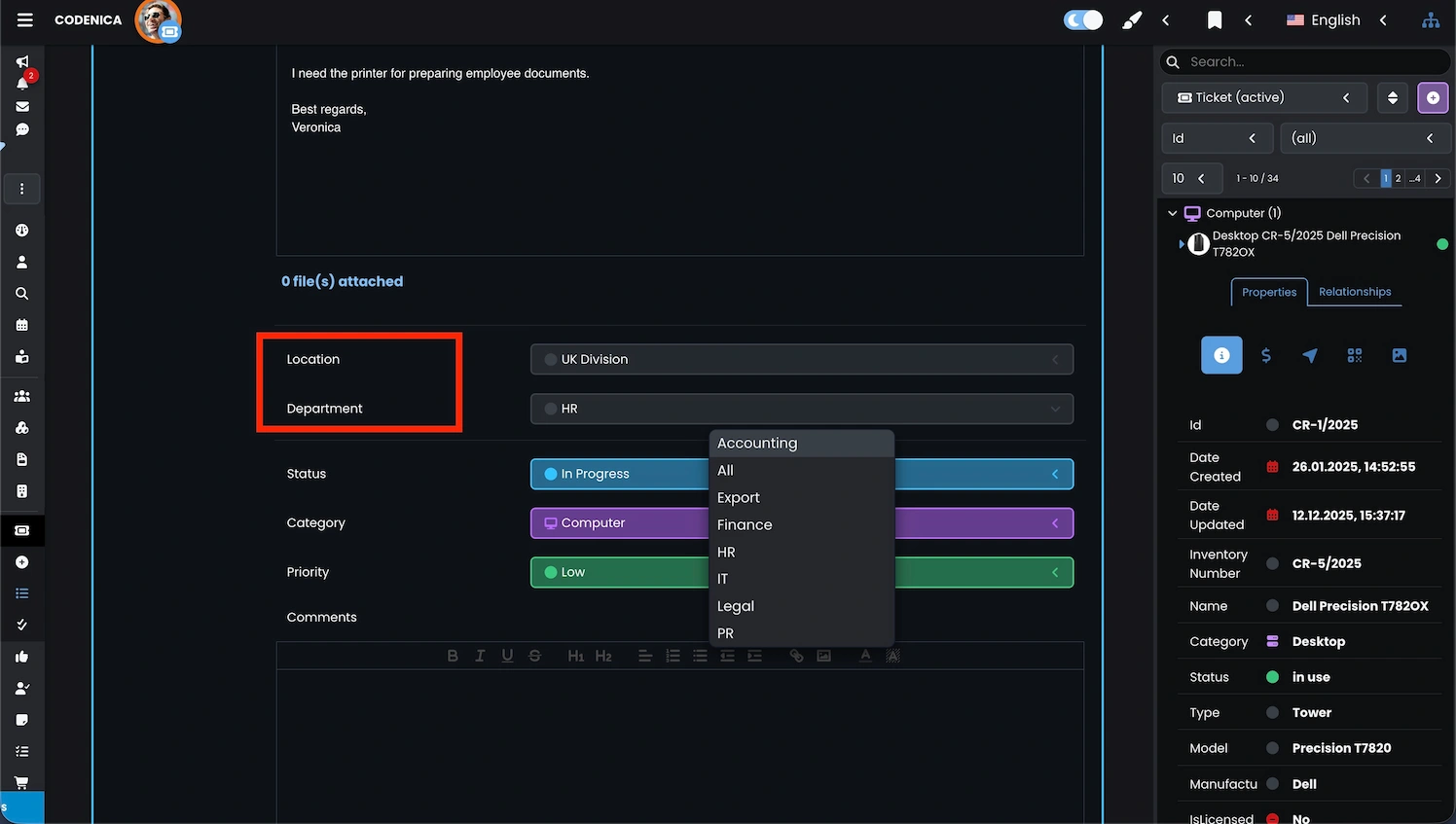
Assigning locations in the ticketing system
Assigning tickets to the appropriate organizational structure is a key element of effective ticket handling. From the moment a request is received, the system can determine exactly which organizational area it belongs to. This keeps ticket queues organized and significantly improves helpdesk and service desk efficiency.
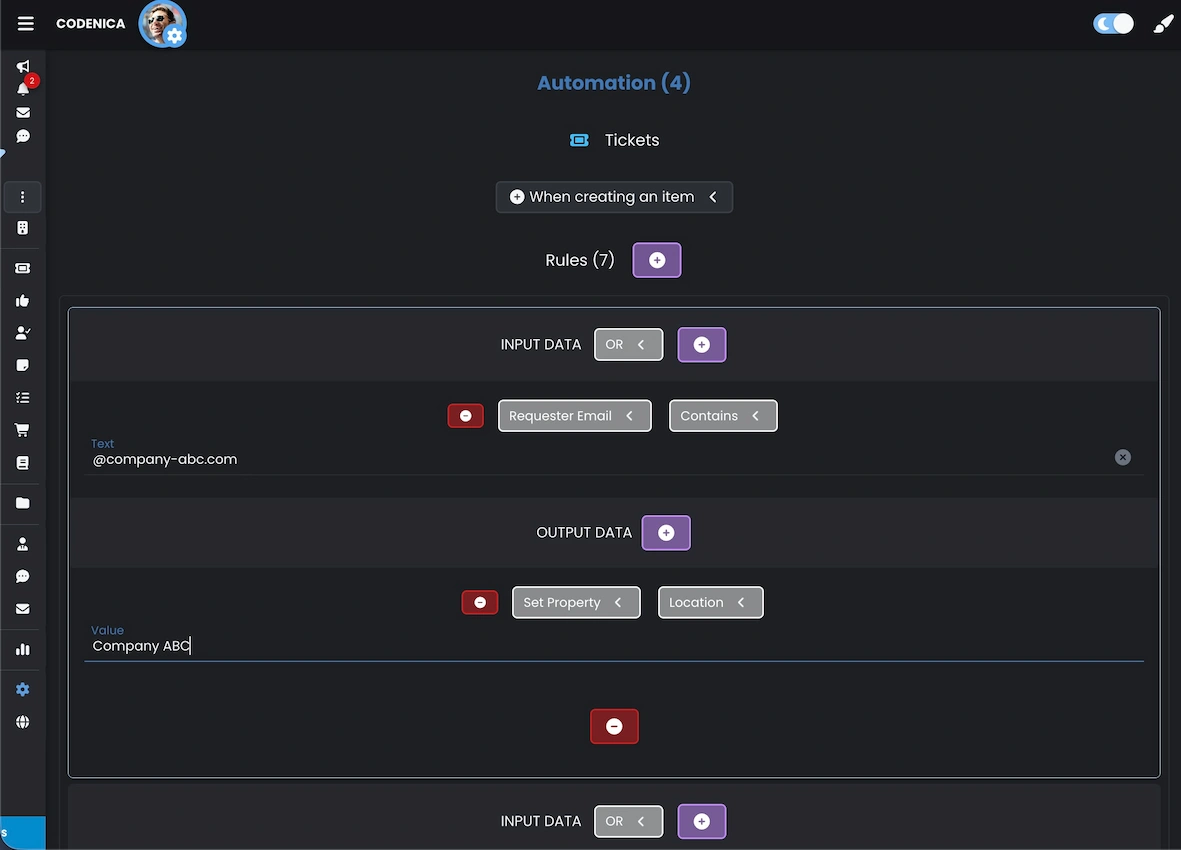
Ticketing system automation
Codenica also supports advanced automation of ticket assignment. Using automation rules and email integration, tickets can be classified automatically at the moment they are created, eliminating human error and speeding up processing-especially in multi-company or multi-department environments.
With automation, tickets are classified correctly without manual intervention. This shortens response times, reduces administrative effort, and supports scalability in high-volume environments. The ticket handling process becomes more structured and predictable.
Assigning locations in the knowledge base
The Codenica knowledge base can be precisely adapted to organizational context by assigning articles to specific structures. This allows creating solutions dedicated to particular companies, teams, or departments, increasing relevance and usability.
This model prevents information overload and content duplication, keeping documentation clear and easy to maintain-even in large environments. This is especially important in multi-client or large internal environments where the number of articles grows over time.
Assigning locations to tasks, notes, requested items, approvals, and confirmations
The same organizational assignment mechanism applies to other system elements such as tasks, notes, requested items, approvals, and confirmations. Each object operates within a clearly defined structure, ensuring process consistency and full information control.
This ensures a consistent, secure, and well-organized environment across all system components.
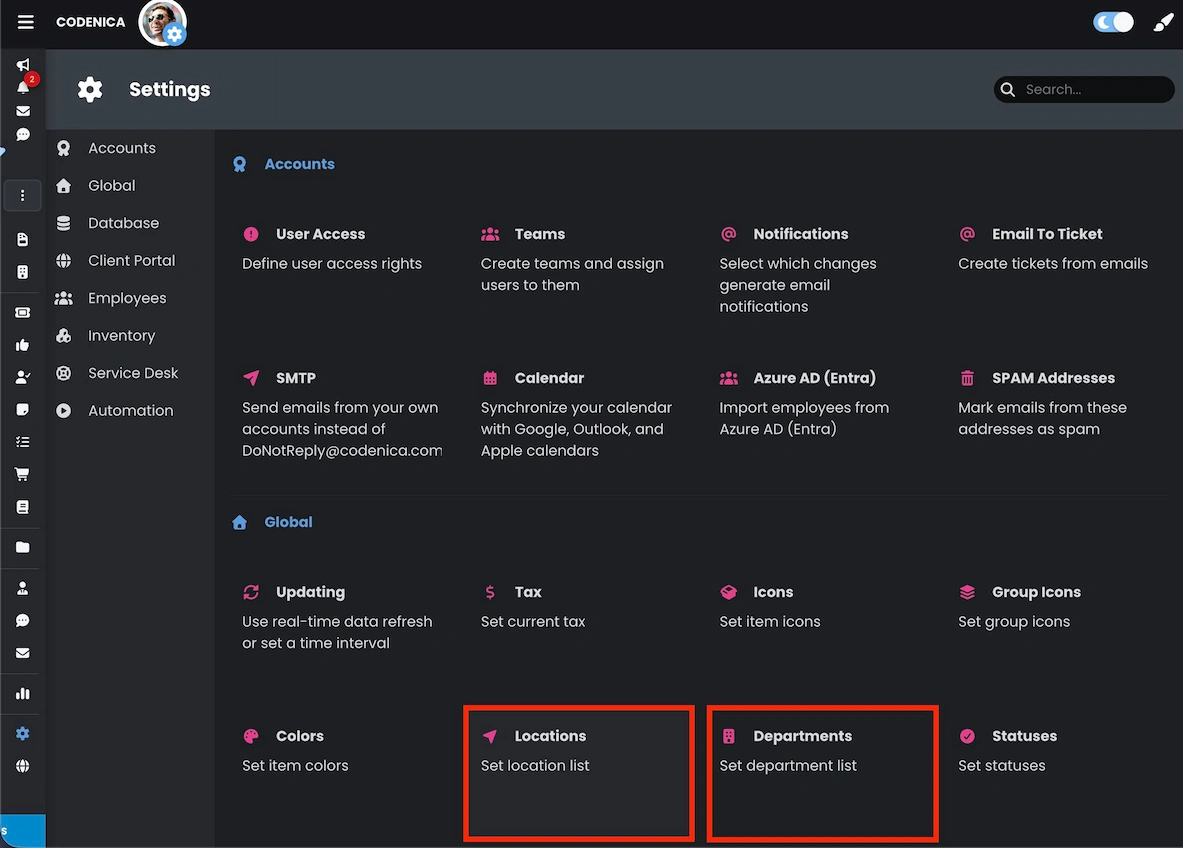
Defining locations and departments
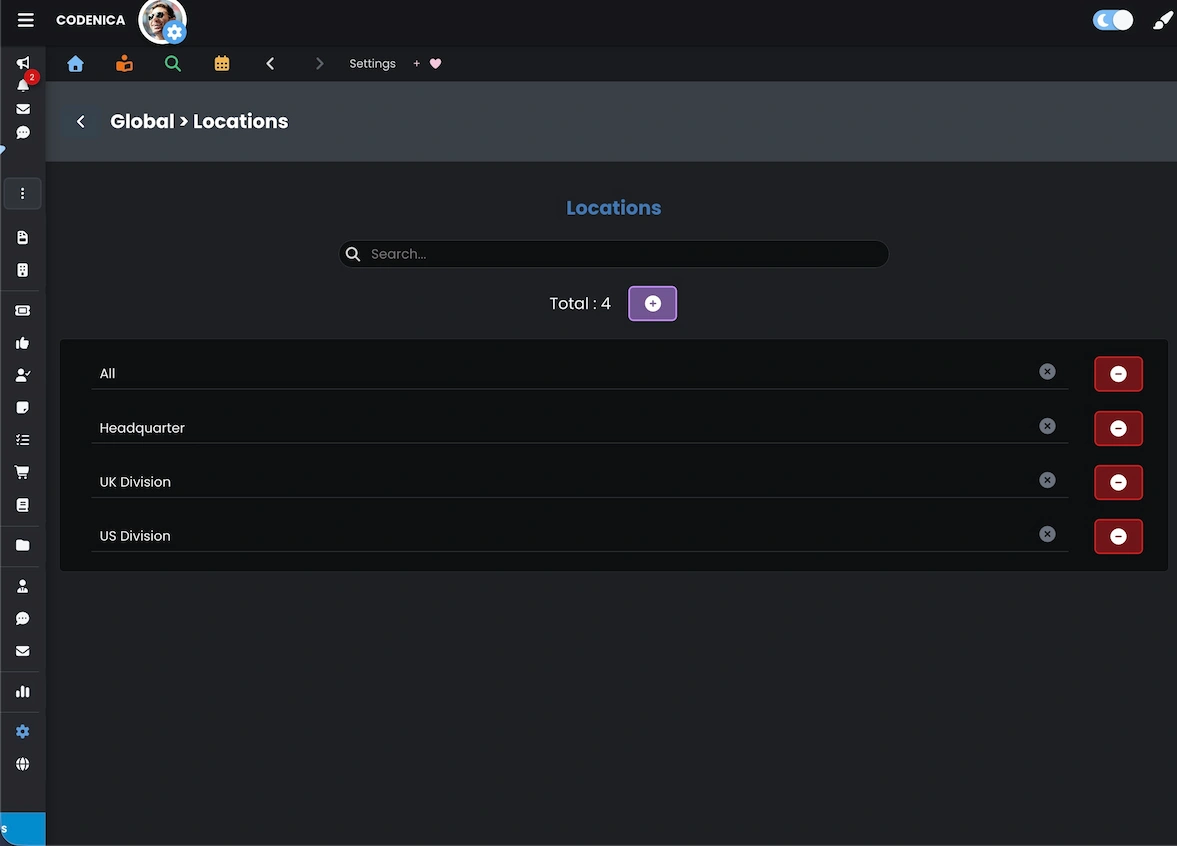
Locations and departments in Codenica ITSM + ITAM are defined as dictionary values in system settings. Configuration is available under System Settings → Global → Locations, and similarly for Departments. This ensures centralized management and consistent selection, preventing typos, inconsistent naming, and accidental duplicates.
IT audits and data imports with location context
IT audits and software audits are essential elements of effective IT asset management. Codenica allows cyclical computer scans and importing audit results directly into the central database, with clear organizational assignment at import time. This is particularly important for organizations performing audits for multiple companies simultaneously, where data separation and clarity are critical. Assigning location context during import ensures audit results remain structured, comparable, and ready for reporting from the very beginning.
Summary
The location mechanism in Codenica ITSM + ITAM is a foundation for structured data management across the system. It supports consistency, visibility control, and scalability for assets, tickets, the knowledge base, audits, and imports. Combined with RBAC, it allows precise control over data access and responsibility scopes while maintaining full administrative oversight of the IT environment.